What Are Dysphoria and Anhedonia?
Unhappiness, dissatisfaction and a more general lack of pleasure can be challenging symptoms to deal with. While national happiness continues to slowly drop, feelings of dissatisfaction or unease with your life can appear to be normal or impossible to escape. If someone you know is dealing with these feelings, they may be living with dysphoria or anhedonia. Learn more about these mental health challenges today and find out how they are linked with addiction.
A related challenge with diagnosing and treating dysphoria and anhedonia is finding the root cause. Both of these situations are typically symptoms of underlying issues. Explore ways to diagnose and treat the underlying struggles that may be causing these feelings in you or someone you love.

Symptoms of Dysphoria
You may be familiar with the feelings of euphoria, such as extreme happiness and a general positive outlook on life. The opposite of this state of mind is dysphoria. Explore the signs and causes of dysphoria and find out how it relates to other mental illnesses and substance abuse issues. Dysphoria negatively affects quality of life and can encourage destructive behaviors in individuals.
Dysphoria isn’t diagnosed as a mental illness on its own, so its causes are often a mental illness or substance abuse issue. Individuals with dysphoria typically exhibit signs of depression or anxiety, such as crying, sleep and appetite disturbances and loss of interest in pleasurable activities. In some cases, suicidal thoughts and actions are also symptoms.
Other symptoms include negative thoughts about future events. Many individuals struggle with fears about implausible situations and have unrealistic expectations about life events. These feelings can negatively affect self-esteem and self-worth.
These symptoms can be very short lived for some individuals, but other cases continue for years. Because of the severity of the symptoms and common underlying issues, it’s important to schedule a visit to a mental health professional to understand more about a particular case of dysphoria and how mental health or substance abuse treatment can help.
Causes and Treatment Options
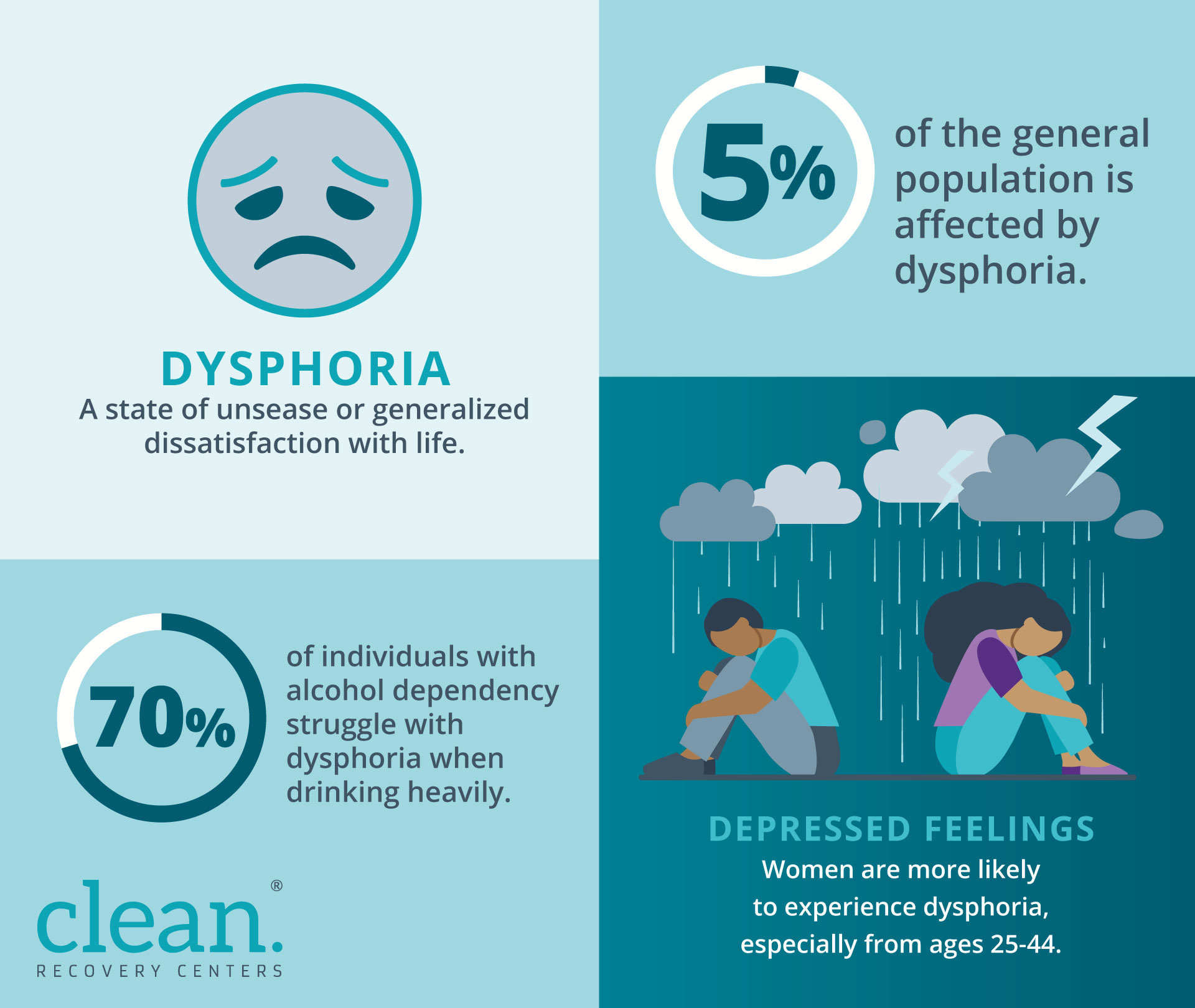
It’s estimated that about 5% of the general population is affected by dysphoria. Causes can include environmental, physical and mental health conditions. Environmental causes include a stressful work environment, family issues or a sudden loss or other tragic incident. Nutritional deficiencies, toxicities and thyroid problems have also been shown to cause feelings of dysphoria.
Women are more likely to experience dysphoria than men, particularly between the ages of 25 and 44. Some cases exhibit all the signs of depression but at lesser severity or a shorter time frame than a clinical diagnosis. These individuals may progress to a clinical depression diagnosis without treatment of the underlying causes. A mental health professional can assist a patient in working through related thoughts and feelings to find the cause of dysphoria. Once the cause is established, a treatment plan can be created.
Many cases are seen as a mild form of clinical depression. Symptoms often end when the underlying cause is treated. This can be a related mental health issue, life event or substance abuse. As many as 70% of individuals with alcohol dependency struggle with feelings of dysphoria, particularly when drinking heavily. Tobacco dependence is also linked with dysphoria. Individuals who have high levels of dependency are more likely to use tobacco products, and individuals with dysphoria are more likely to turn to cigarettes and other tobacco products as a coping mechanism.
Substance abuse treatment services can reduce or remove symptoms of dysphoria for many individuals struggling with a substance abuse issue. Most treatment options focus on treating the underlying issue instead of directly treating the thoughts and feelings associated with dysphoria. Once the underlying issues are treated, thoughts and feelings of dysphoria typically go away quickly.
Symptoms of Anhedonia
A similar emotional issue that affects many individuals is anhedonia. Just like dysphoria, anhedonia isn’t diagnosed as a mental health disorder on its own, but is a common symptom of a depressive disorder or substance abuse challenge. Individuals who experience anhedonia lose interest in common activities, but in ways that are distinct from dysphoria.
Unlike dysphoria, anhedonia is characterized more by the lack of feelings than depressed feelings. These symptoms can be divided into physical and social anhedonia. Physical signs include little or no pleasure from positive tactile experiences. These can include touching, eating and sex. Social symptoms include withdrawal, lack of positive feelings about someone you love and difficulty adjusting to a specific social situation.
Some individuals who experience anhedonia attempt to self-medicate with alcohol, drugs or risky behaviors. These behaviors attempt to restore normal levels of emotional response to stimuli and restore an individual’s sense of normal emotions. Without treatment, individuals with anhedonia can develop substance abuse issues.
These symptoms are core elements of clinical depression, so many individuals who experience feelings of anhedonia are prescribed counseling, medication and other treatment options. Mental health professionals look for underlying causes that point to either major depressive disorder or substance abuse. Treating these challenges can reduce or remove feelings of anhedonia.
There are other mental health challenges related to anhedonia. Be sure to work with a mental health provider to diagnose the cause of these feelings. Here are some commonly related mental disorders:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Psychosis
- Schizophrenia
- Anorexia nervosa
- Substance abuse
Individuals with one or more of these mental illnesses or other signs linked with these illnesses should work with a professional immediately to receive a diagnosis and treatment plan. Treating the disorder will often reduce or eliminate feelings of anhedonia.

Treatment and Prevention Strategies
As many as one third of individuals with clinical depression engage in substance abuse. Self-medication with drugs or alcohol is a common symptom of depression and can cause lasting challenges for individuals. Mental health professionals can assist individuals on the road to recovery by treating the symptoms of anhedonia, any related substance abuse issues and the underlying causes of depression.
Individuals who have recently experienced a tragic or stressful life event are more likely to experience feelings of anhedonia. These feelings also correlate with other major illnesses and mental health disorders, such as eating disorders and other depressive disorders.
It’s essential for individuals to treat the substance abuse and mental health aspects of anhedonia. Focusing on the symptoms can miss the root cause of these feelings, which leads many individuals to self-medication and destructive coping strategies. If left untreated, these self-destructive behaviors can quickly escalate and lead to more serious emotional, social and physical issues.
Receive Quality Care at Clean Recovery Centers
At Clean Recovery Centers, we offer treatment and stabilization for individuals experiencing physical, emotional and social issues due to substance abuse challenges. Our Three-Phase Approach offers holistic healing that balances evidence-based practices and expert medication management to restore an individual in as little as three to six months. This proven treatment approach has helped individuals overcome dysphoria, anhedonia and related substance issues.
There is hope for individuals experiencing dysphoria or anhedonia. If you’re experiencing these feelings or know a loved one who may be, don’t hesitate to contact us at Clean Recovery Centers. Our mission is to assist individuals with their substance abuse and related mental health issues. We strive to not only provide freedom from these emotional issues, but we also work toward full recovery from underlying addictions and mental health challenges.
Infographic: What are Dysphoria and Anhedonia?
View the full Infographic about symptoms and statistics of Dysphoria and Anhedonia.



